Figure 1: Satellite Communication Basics

C-band satellite transmissions occupy the 4 to 8 GHz frequency range. These relatively low frequencies translate to larger wavelengths than Ku-band or Ka-band. These larger wavelengths of the C-band mean that a larger satellite antenna is required to gather the minimum signal strength, and therefore the minimum size of an average C-band antenna is approximately 2-3 meters in diameter as shown in Figure 2.


Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) Satellites
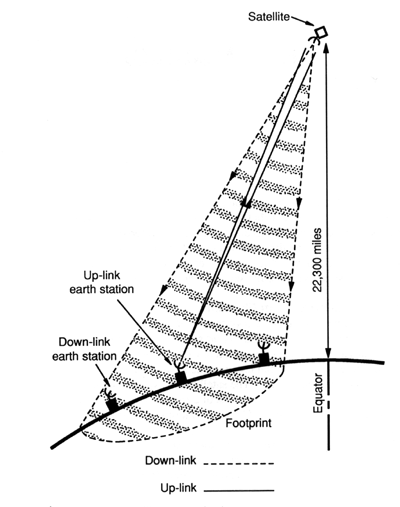
Today, the overwhelming majority of satellites in orbit around the earth are positioned at a point 22,238 miles above the earth's equator in a special type of geosynchronous earth orbit (GSO) known as Geostationary earth orbit (GEO), or what is sometimes called Clarke orbit. This is in honor of Arthur C. Clarke, the man who first suggested in 1945 that satellites in geosynchronous orbits could be used for communications purposes. As shown in Figure 4, it is at the precise distance of 22,238 miles that a satellite can maintain an orbit with a period of rotation around the earth exactly equal to 24 hours. Since the satellites revolve at the same rotational speed of the earth, they appear stationary from the earth’s surface. That's why most earth station antennas (satellite dishes) don't need to move once they have been properly aimed at a target satellite in the sky. The mathematical derivation of the Clarke orbit is a straight-forward calculus problem.(1)

Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites
Proposed LEO satellites are divided into three categories: little LEOs, big LEOs, and Mega-LEOs. LEOs will orbit at a distance of only 500 to 1000 miles above the earth. This relatively short distance reduces transmission delay to only .05 seconds and further reduces the need for sensitive and bulky receiving equipment. Little LEOs will will operate in the 800 MHz (.8 GHz) range, big LEOs will operate in the 2 GHz or above range, and Mega-LEOs will operate in the 20-30 GHz range. The higher frequencies associated with Mega-LEOs translates into more information carrying capacity and the capability of real-time, low delay video transmission. Microsoft Corporation and McCaw Cellular (now known as AT&T Wireless Services) have partnered to deploy 840 satellites to form Teledesic, a proposed Mega-LEO satellite network.
High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Platforms
Experimental HALE platforms are essentially highly efficient and lightweight airplanes carrying communications equipment that will act as very low earth orbit geosynchronous satellites. These crafts will be powered by high efficiency turbine engines or a combination of battery and solar power. At an altitude of only 70,000 feet, HALE platforms will offer transmission delays of less than .001 seconds and even better signal strength for very lightweight hand-held receiving devices.(2)
Orbital Slots
With more than 200 satellites up there in geosynchronous orbit, how do we keep them from running into each other or from attempting to use the same location in space? To tackle that problem, international regulatory bodies like the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) and national government organizations like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) designate the locations on the geosynchronous orbit where communications satellites can be located. These locations are specified in degrees of longitude and are known as orbital slots. In response to the huge demand for orbital slots, the FCC and ITU have progressively reduced the required spacing down to only 2 degrees for C-band and Ku-band satellites.
Return to the Main Menu.